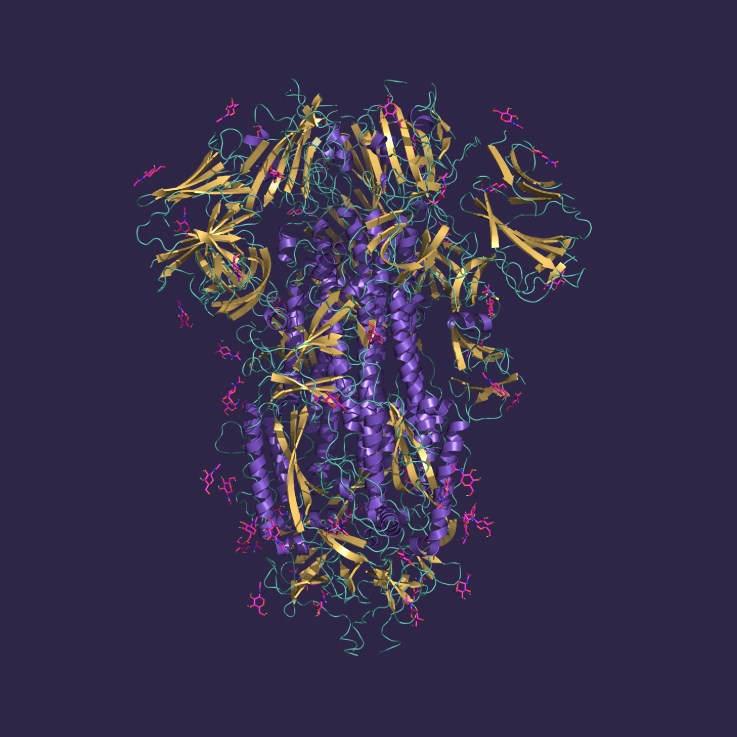
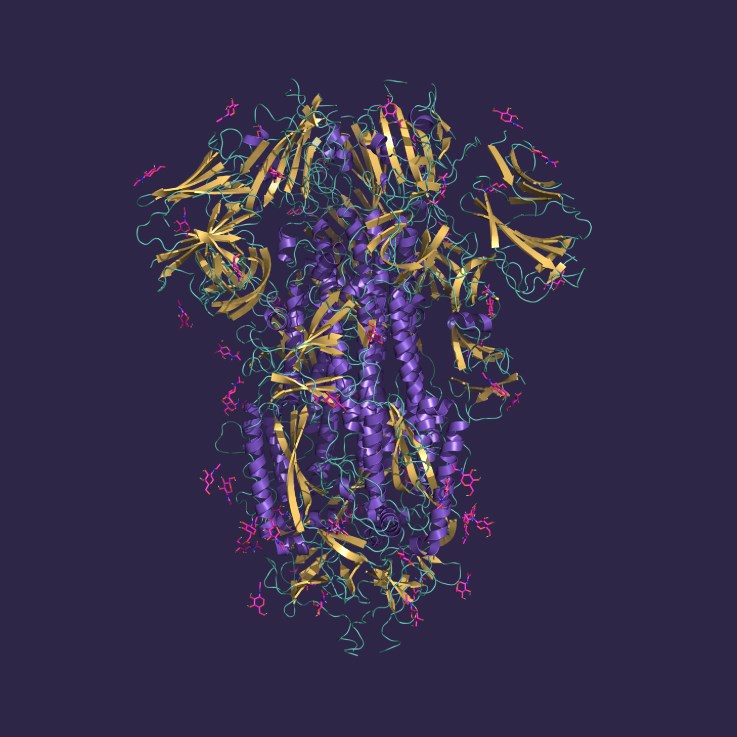
Glycoproteins expressed in eukaryotic cells typically contain N- and O-linked oligosaccharide groups attached to amino acid side chains of the polypeptide backbone. These glycans are not just structural decorations but play essential roles in stability, half-life, secretion, and biological activity, making glycoprotein integrity and purity a critical quality attribute in therapeutic manufacturing.
Erythropoietin (EPOs) is one of the most commercially successful recombinant glycoproteins, used globally in the treatment of anemia. Its therapeutic effectiveness depends heavily on extensive sialylation, which prolongs circulation time in the bloodstream and reduces clearance. Engineered long-acting variants such as darbepoetin have been developed with additional glycosylation sites to further extend half-life, reducing the frequency of dosing and improving patient compliance.
Recombinant clotting factors, including Factor VIII and Factor IX, are central to the treatment of hemophilia. These proteins are heavily glycosylated, and their glycan structures are vital for proper secretion, stability, and biological activity. Maintaining correct glycosylation during manufacturing reduces the risk of immunogenic responses and ensures consistent therapeutic function. The complexity of Factor VIII, in particular, makes it one of the most challenging glycoproteins to produce and purify at scale.
Enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs) are used in the treatment of rare lysosomal storage disorders, where enzyme deficiencies lead to the accumulation of toxic substrates in cells. For these therapies, glycosylation is not only important but essential, as specific motifs such as mannose-6-phosphate act as targeting signals that allow the therapeutic enzyme to be delivered to the lysosome. Without these glycans, the therapy cannot reach its site of action, making glycan integrity a critical quality attribute.
Several recombinant hormones and cytokines also depend on glycosylation to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. For example, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) requires glycan structures for stability and bioactivity, while glycoengineered forms of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) demonstrate improved serum half-life and reduced dosing requirements compared to their non-glycosylated counterparts. In these cases, glycosylation directly translates into improved pharmacokinetics and enhanced patient benefit.